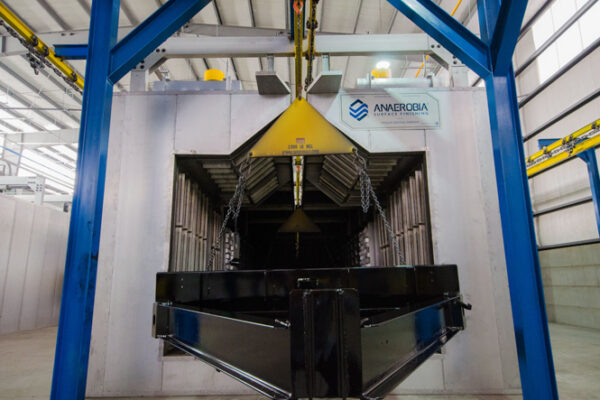
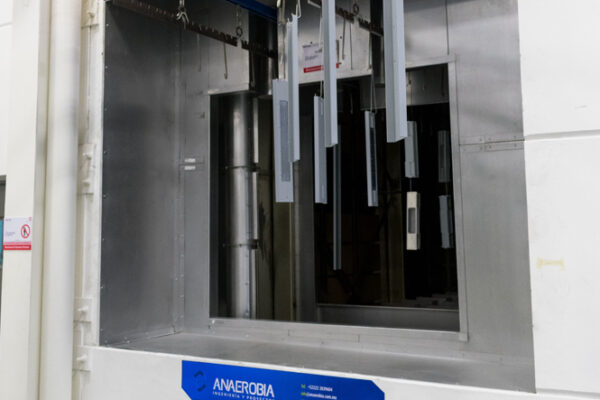
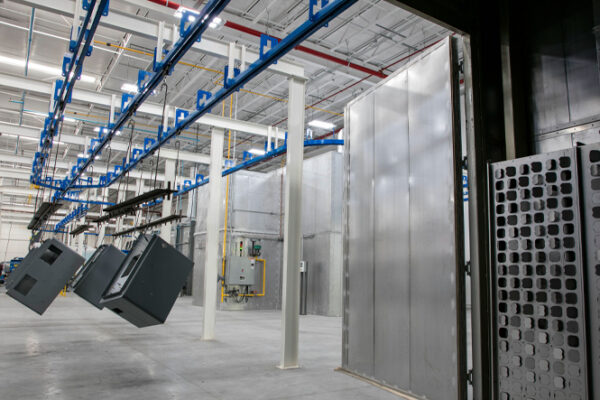
What are drying and curing ovens?
Drying and curing ovens are thermal processing equipment that use controlled heat to remove moisture from surfaces (drying) and to harden or stabilize certain coatings or compounds (curing). During the drying phase, the oven evaporates solvents from paint, resins, or other coatings, while in the curing phase, heat activates chemical reactions that harden or stabilize the materials. The ability to control factors such as temperature, air circulation, and treatment time allows these ovens to be adapted to different types of processes and materials.
We enhance global industry through specialized
engineering and advanced technology.
Benefits of drying and curing ovens
Even and controlled drying:
Thanks to their thermal distribution system, ovens ensure uniform drying across the entire surface, preventing defects such as bubbles, cracks, or improperly cured areas.
Improvement in finish quality:
They achieve superior adhesion and durability in coatings such as paint, powder, or resin, ensuring a more durable and professional finish.
Greater efficiency in time and productivity:
They significantly reduce drying and curing times compared to traditional methods, resulting in faster and more efficient production cycles.
Versatility in materials and applications:
They are suitable for various types of materials (metals, plastics, ceramics, etc.) and can be adapted to diverse industrial processes, ranging from automotive to electronic manufacturing.
Experience: Our team has the necessary training and expertise to face the challenges of the industry.
Local Support: We are present in the country’s industrial hubs to provide close and timely assistance to our clients.
Standards:Our equipment complies with international and national regulations.
Types of ovens
There are various types of drying and curing ovens, such as convection ovens, catalytic ovens, and infrared ovens. Each type is suitable for different applications, depending on the material characteristics and the specific requirements of the treatment process.
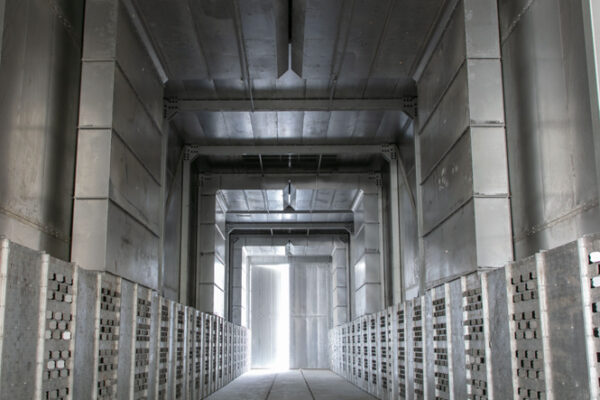
Drying and curing processes can be performed using convection ovens. A convection oven is equipment where the chamber (working area) is heated by high-temperature air, which is supplied and distributed to generate heat exchange between the process air and the materials being treated, raising the substrate temperature according to process parameters.
This type of oven operates by transferring heat from a fluid (air) to a solid. With proper air management design, it provides uniform temperature across the entire surface of the part, even if its geometry is complex. The heat increase can be supplied through the combustion of fuels such as natural gas or propane, or via electric resistors, among other methods. Balancing the airflow contributes to greater energy efficiency and better process control. Advantages offered by convection ovens include:
- Uniform temperature: Hot air circulates through the oven, distributing evenly over the surfaces of the products. This ensures that all items inside the oven receive similar temperatures, resulting in uniform heating or curing. Temperature uniformity is crucial for consistent results, avoiding overheated or cold spots that could damage or affect product quality.
- Balanced airflow: Convection ovens are designed to maintain a balanced and constant airflow. This means hot air is efficiently distributed throughout the oven, improving heat transfer to the products.
- Flexibility for substrate types: A continuous convection oven can process products of different sizes and shapes while maintaining a consistent working profile throughout the process. In this type of oven, the product moves continuously through the oven, allowing the hot airflow to adapt to various object sizes without significant adjustments. This offers great flexibility to treat a wide variety of products without needing equipment modifications for each specific geometry.
Catalytic ovens are one of the types available for carrying out the curing process. This type of oven differs from conventional heating systems by having an internal catalytic panel that emits infrared radiation. These heat waves travel in random straight lines and are easily absorbed by inorganic surfaces such as powder coatings and liquid paint.
Catalytic ovens operate using both electricity and gas. Electricity is used to preheat the oven. During startup, the enclosed electric heater is activated for a period of 15–20 minutes. Once the catalyst reaches the proper temperature, gas is introduced through the safety valve to initiate the catalytic heating process. The gas enters the heater via the dispersion tube and is distributed through the dispersion screen. Then, the gas diffuses through the insulation, coming into contact with the catalyst to start the catalytic reaction. Infrared energy is emitted along with CO2 and water vapor. Some key benefits of a catalytic oven include:
- Lower operating temperature: Catalytic heaters operate at a lower temperature than conventional heating systems, allowing for more uniform heat distribution.
- Safe use with hazardous materials/gases: These heaters do not produce an open flame, making them safe for use in environments where hazardous materials or gases are handled. This feature minimizes the risk of fire or explosion, making them an ideal option for chemical, pharmaceutical, and other industries that require extra safety precautions.
- Clean emissions: Catalytic heaters provide cleaner combustion, emitting only carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor, without releasing harmful pollutants or compounds into the environment. This significantly reduces environmental impact and improves air quality in nearby areas.
Infrared ovens are an alternative method for carrying out the curing process. In these ovens, heat transfer can occur in three ways: conduction, convection, or radiation. Conduction requires direct contact between two objects—the heat source and the surface to be cured. Convection relies on heat transfer through the air. Infrared (IR) radiant heating is distinguished by its mode of operation. Unlike other systems, it does not require a medium to transfer heat, as it heats objects directly. This feature makes it extremely efficient.
Infrared ovens emit thermal energy via electromagnetic waves of varying wavelengths, classified into long, medium, and short waves.
- Long wavelength: Long waves have low intensity and a response time of about 5 minutes. Although their energy density is lower, they are efficiently absorbed by organic coatings. The energy concentrates on the material’s surface, transmitting little energy to the substrate. This makes them ideal for surface drying or thin layers, since the energy does not penetrate deeply into the material.
- Medium wavelength: Medium waves have moderate energy density, making them ideal for curing coatings. They penetrate the coating but not the substrate, allowing curing to start from the inside out. The response time is fast—around 60 seconds—enabling efficient curing without affecting the substrate.
- Short wavelength: Short waves have high energy density, which makes them ideal for specialized applications requiring fast and deep treatment. With an instant response time, as seen in T3 lamps, the energy penetrates the coating and reaches the substrate, where it converts to heat. This makes it useful for preheating and processes needing deep, controlled heating.
Infrared ovens offer several advantages, such as reducing cycle times without compromising curing properties, since they allow rapid heating to higher temperatures in a shorter timeframe. This efficiency is due to their ability to transfer heat effectively, optimizing the curing process. Additionally, zoning in these ovens allows precise area control, with adjustable heating curves to suit the specific needs of each application. This contributes to an almost immediate response time, making the curing process faster. Thanks to these features, infrared ovens are ideal for processes requiring fast curing and high temperatures, improving efficiency and reducing production times.
Why are drying and curing ovens important?
Drying and curing ovens are essential in industrial finishing processes, allowing complete control over the heat treatment of coated or treated materials. Their benefits in terms of quality, durability, and efficiency make them an indispensable tool in numerous industries. The variety of types and configurations available enables these ovens to adapt to specific needs, helping optimize production and ensure high-quality final products.

Standards
Our ovens comply with international regulations and quality and safety requirements.
We design paint booths tailored to the needs and demands of each client to ensure compliance with international standards (NFPA, OSHA, ETL, FM GLOBAL, ATEX, etc.).
Qualified and experienced team: Project Managers certified by IPMA.




If you require additional information, please send an email.
Business Partnerships
Experience that supports us
FAQ'S
In industrial painting, drying is the physical process where the solvent or water in the paint evaporates, leaving it dry to the touch. Curing, on the other hand, is a chemical process in which the paint components react to form a strong and fully hardened film. While drying prepares the surface, curing ensures its durability, adhesion, and final resistance.
The curing time for paint in an industrial oven depends on the type of coating and the temperature applied, but it generally ranges between 10 and 60 minutes. For liquid paints such as epoxies or polyurethanes, curing typically occurs between 120°C and 160°C for 20 to 60 minutes. For powder coatings, the process is faster, with times from 10 to 30 minutes at temperatures between 160°C and 200°C. These ranges ensure a fully hardened finish with maximum resistance and durability.
A drying and curing oven requires regular maintenance that includes cleaning filters, fans, and ducts to prevent the buildup of dust or flammable residues; inspecting and calibrating temperature sensors and control systems to ensure even heating; checking thermal insulation and seals to avoid heat leaks; inspecting burners or electric resistors; and performing safety tests on gas or electrical shutoff systems. Conducting preventive maintenance periodically minimizes unexpected downtime and extends the equipment’s lifespan.
To choose the right oven, first consider the type of material and coating you’ll be working with (liquid, powder, epoxy, etc.), as well as your daily production volume. Define the dimensions of the parts to be processed and the available space in your facility. Also evaluate the required curing temperature and time, as this will determine whether you need a convection, infrared, or combination oven. Additionally, make sure the oven features precise control systems, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance. A specialized supplier can help you customize the solution to meet your specific needs.